Compressing Redshift columnar data even further with proper encodings
Basics
Amazon Redshift is database aimed primarily on analytics and OLAP queries.
One of its key features is storing data in columnar format, in other words keeping one column’s data adjacent on disk.
That enables storing higher volumes of data compared to row formats due to encoding algorithms and one column’s homogenous data nature (it compresses very well).
By default when you initially create and populate a table, Redshift chooses compression algorithms for every column by default.
See more about Redshift compression encodings.
Question default compression options
I wanted to know if it was possible to apply better encoding algorithms and compress data even further.
Luckily we have ANALYZE COMPRESSION command:
Performs compression analysis and produces a report with the suggested compression encoding for the tables analyzed. For each column, the report includes an estimate of the potential reduction in disk space compared to the current encoding.
ANALYZE COMPRESSION hevo.wheely_prod_orders__backup COMPROWS 1000000 ;
Here is the sample output:
| Table | Column | Encoding | Est_reduction_pct |
|---|---|---|---|
| wheely_prod_orders | _id | raw | 0.00 |
| wheely_prod_orders | status | zstd | 49.93 |
| wheely_prod_orders | new_client | zstd | 39.04 |
| wheely_prod_orders | markup | zstd | 99.66 |
| wheely_prod_orders | country_code | zstd | 60.67 |
| wheely_prod_orders | tips | zstd | 83.34 |
| wheely_prod_orders | tags | zstd | 35.80 |
Your next steps would be:
- CREATE a new table with proposed encodings (possibly new dist/sort keys)
- INSERT data to a new table (perform a deep copy)
- Perform tests and benchmarks
- Interchange tables, delete old table
Wrap it up into automatic macro
Now when it comes to automating routine operations or performing it on a number of tables frameworks such as dbt come very handy.
It is possible to automate the whole cycle of operations and even put it on regular basis with dbt macro as simple as this:
{{ redshift.compress_table('hevo',
'wheely_prod_orders',
drop_backup=False,
comprows=1000000) }}
See the description of dbt Redshift package as well as compression macro source code.
Let us examine what is does underneath:
-- ensure new table does not exist yet
drop table if exists "hevo"."wheely_prod_orders__compressed";
-- CREATE new table with new encodings
create table "hevo"."wheely_prod_orders__compressed" (
-- COLUMNS
"_id" VARCHAR(512) encode raw not null ,
"status" VARCHAR(512) encode zstd ,
"new_client" VARCHAR(512) encode zstd ,
"sorted_at" TIMESTAMP WITHOUT TIME ZONE encode az64 ,
"transfer_other_zone_id" VARCHAR(512) encode lzo ,
"ts" VARCHAR(512) encode lzo ,
...
-- CONSTRAINTS
, PRIMARY KEY (_id)
)
--KEYS
-- DIST
diststyle key
distkey("_id")
-- SORT
compound sortkey("_id")
;
-- perform deep copy
insert into "hevo"."wheely_prod_orders__compressed" (
select * from "hevo"."wheely_prod_orders"
);
-- perform atomic table interchange
begin;
-- drop table if exists "hevo"."wheely_prod_orders__backup" cascade;
alter table "hevo"."wheely_prod_orders" rename to "wheely_prod_orders__backup";
alter table "hevo"."wheely_prod_orders__compressed" rename to "wheely_prod_orders";
commit;
Assess the results
I have performed compression routine on a number of tables and now it is time to examine the results.
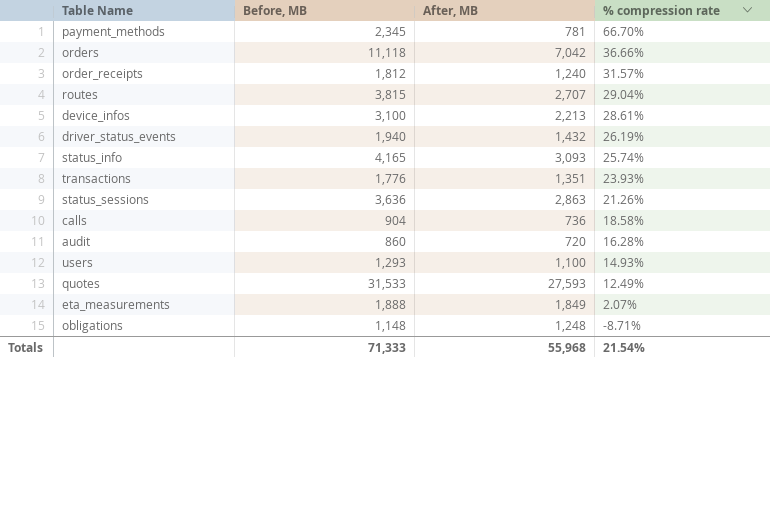
The compression rate varies widely from 67% to -9% which tells us automatic compression is not suitable for every case.
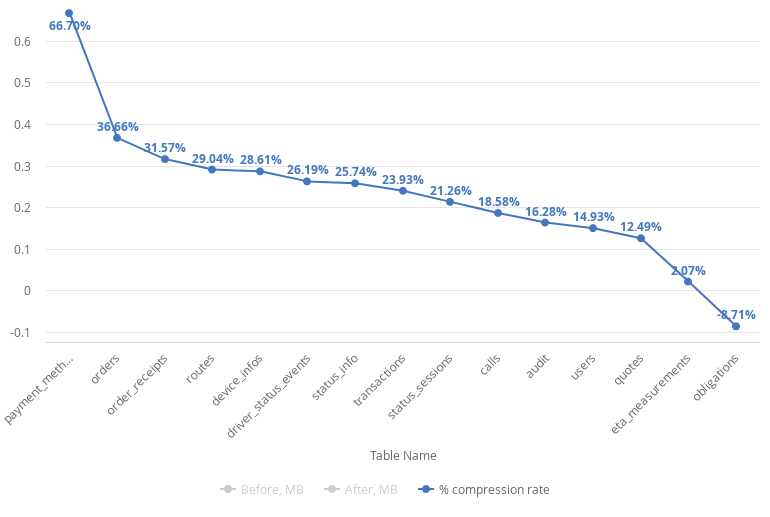
Even though we have obligations table with negative result we see 21.5% on average disk space usage reduction.
Before you apply any changes make sure to assess query performance and short-list tables which are to be compressed. In my case I am compressing every table except obligations which I will leave as-is.
Key outputs
- Thoroughly assess the result and queries performance. The main goal is still retain query speed and performance while improve disk usage and IO.
- Consider ZSTD compression algorithm. According to Redshift doc page:
Zstandard (ZSTD) encoding provides a high compression ratio with very good performance across diverse datasets. ZSTD works especially well with CHAR and VARCHAR columns that store a wide range of long and short strings, such as product descriptions, user comments, logs, and JSON strings. Where some algorithms, such as Delta encoding or Mostly encoding, can potentially use more storage space than no compression, ZSTD is very unlikely to increase disk usage.
- Wrap it up into a macro that could be run automatically on a regular basis.
Feel free to leave any comments or questions.
